Fetal Malnutrition: Causes, Risks, and Prevention
1. What Is Fetal Malnutrition?
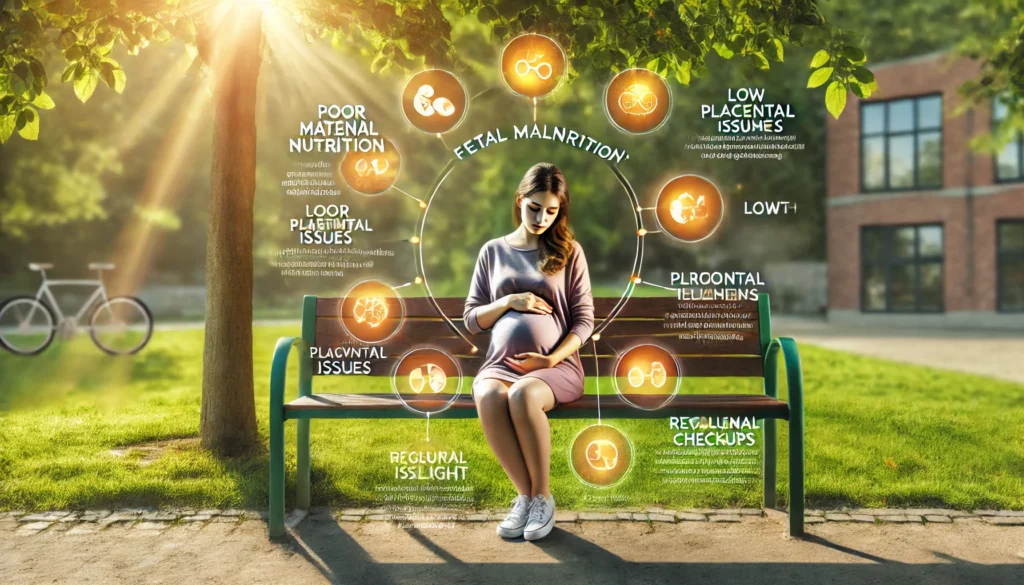
Fetal malnutrition occurs when a baby does not receive adequate nutrients in the womb, leading to slow growth and developmental issues. This condition can increase the risk of complications both during pregnancy and after birth.

2. Causes of Fetal Malnutrition
Several factors can contribute to fetal malnutrition, including:
- Poor Maternal Nutrition: Inadequate intake of essential nutrients such as protein, vitamins, and minerals can affect fetal development.
- Placental Insufficiency: If the placenta does not function properly, it may not supply enough oxygen and nutrients to the baby.
- Maternal Health Conditions: Diseases like diabetes, high blood pressure, and anemia can hinder nutrient absorption and distribution.
- Multiple Pregnancies: Carrying twins or more can strain the mother’s body, leading to insufficient nutrition for each baby.
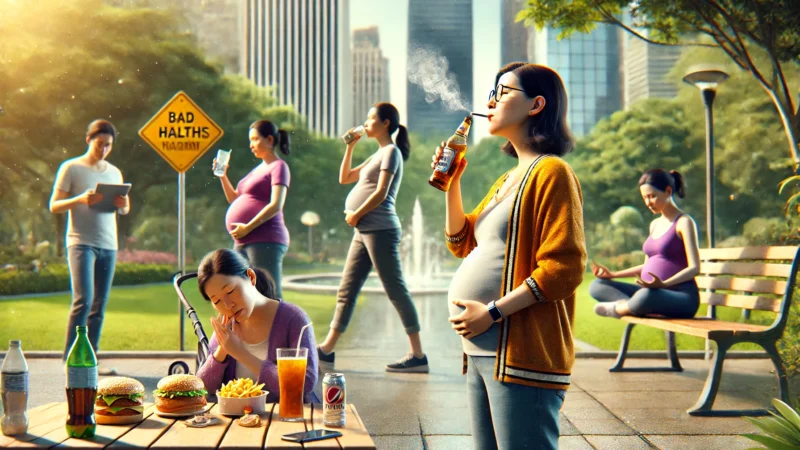
- Smoking, Alcohol, and Drug Use: These substances restrict blood flow to the fetus, affecting growth.
- Stress and Poor Lifestyle Choices: High stress levels and lack of rest can negatively impact fetal nutrition.
3. Effects of Fetal Malnutrition
Fetal malnutrition can lead to severe health complications, such as:
- Low Birth Weight: Babies with inadequate nutrition may be born underweight, making them more vulnerable to health issues.
- Weakened Immune System: Malnourished infants may have a weaker immune system, increasing their risk of infections.
- Delayed Physical and Mental Development: Nutritional deficiencies can affect brain development and physical growth.
- Higher Risk of Chronic Diseases: Poor nutrition in the womb has been linked to long-term conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and obesity.
- Increased Risk of Stillbirth or Preterm Birth: Severe malnutrition can lead to premature delivery or pregnancy complications.
4. How to Prevent Fetal Malnutrition
To ensure healthy fetal development, expectant mothers should:
- Maintain a Balanced Diet: Include a variety of nutrient-rich foods, such as lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and dairy products.
- Take Prenatal Supplements: Folic acid, iron, and calcium supplements can help meet nutritional needs.
- Attend Regular Prenatal Checkups: Monitoring fetal growth allows early detection and management of potential issues.
- Avoid Harmful Substances: Refrain from smoking, alcohol, and drugs to ensure a healthy pregnancy.
- Manage Chronic Conditions: If the mother has diabetes or hypertension, proper medical care is essential.
- Practice Stress Management: Yoga, meditation, and adequate rest can support overall maternal and fetal well-being.
5. When to Seek Medical Help
Mothers should consult a doctor if they experience:
- Unusual weight loss or lack of weight gain during pregnancy.
- Reduced fetal movement or growth concerns.
- Chronic illnesses that may affect fetal development.
- Symptoms of nutrient deficiencies, such as dizziness, extreme fatigue, or poor appetite.
Conclusion
Fetal malnutrition is a serious concern that can impact a baby’s health even after birth. By following a proper diet, attending prenatal checkups, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, expectant mothers can help prevent malnutrition and ensure their baby’s well-being. If there are any concerns about fetal growth, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for timely intervention.