Hidden Signs of Gestational Diabetes You Shouldn’t Ignore
Gestational diabetes is a metabolic disorder that occurs during pregnancy when the body does not produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. This condition typically develops between the 24th and 28th weeks of pregnancy and can impact both the mother and the baby if not detected and managed in time.

Causes of Gestational Diabetes
During pregnancy, hormonal changes can reduce insulin’s effectiveness in controlling blood sugar, leading to increased glucose levels. Some risk factors include:
- Being overweight or obese before pregnancy: Women with a high body mass index (BMI) are at a greater risk of developing gestational diabetes.
- Family history of diabetes: If a close relative has diabetes, your risk increases.
- Age factor: Women over 25 years old are more likely to develop the condition.
- Previous history of large babies: If you have previously given birth to a baby weighing over 4.1 kg (9 lbs), your risk is higher.
- Ethnicity: Women of Asian, African, Hispanic, and Pacific Islander descent are at greater risk.
Symptoms of Gestational Diabetes
The symptoms of gestational diabetes are often mild or mistaken for common pregnancy changes. However, some warning signs include:
- Increased thirst: Constant thirst that is difficult to quench may indicate high blood sugar.
- Frequent urination: While frequent urination is common in pregnancy, a sudden increase may be a warning sign.
- Extreme fatigue: If you feel excessively tired even after getting enough rest, it could be a sign of high blood sugar.
- Nausea: Although nausea is normal in early pregnancy, gestational diabetes can also cause this symptom.
- Recurring infections: Frequent urinary tract, vaginal, or skin infections may be linked to gestational diabetes.
- Blurred vision: High blood sugar levels can affect eyesight and cause blurred vision.
Because these symptoms can be easily overlooked or mistaken for typical pregnancy discomforts, regular prenatal checkups and necessary tests are essential for early detection and management.
Blood Sugar Testing During Pregnancy
Between the 24th and 28th weeks of pregnancy, doctors typically recommend a glucose screening test to check for gestational diabetes. The process involves:
- Glucose challenge test: You will drink a glucose-containing solution, and your blood sugar level will be measured after one hour. If the result is higher than normal, a glucose tolerance test will be required.
- Glucose tolerance test: You will fast overnight, then consume a glucose solution, and your blood sugar levels will be checked at different intervals over three hours. If two or more readings exceed the normal range, you will be diagnosed with gestational diabetes.
Managing and Treating Gestational Diabetes
If diagnosed with gestational diabetes, you should follow these steps to control your blood sugar levels:
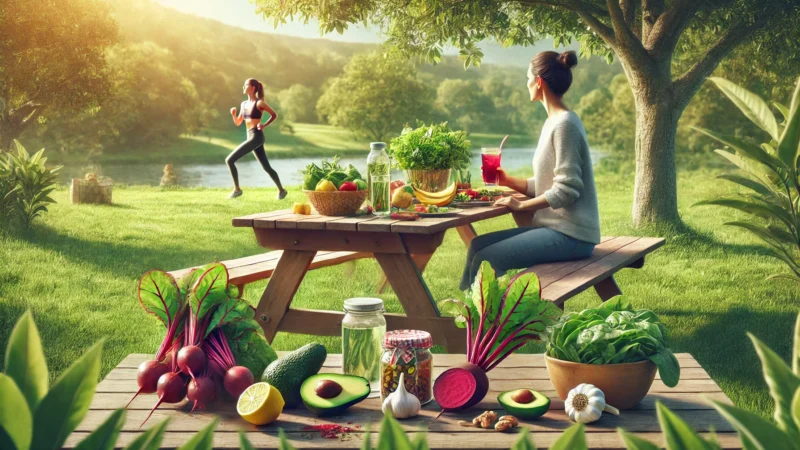
- Healthy diet: Eat plenty of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins while reducing sugar and refined carbohydrates.
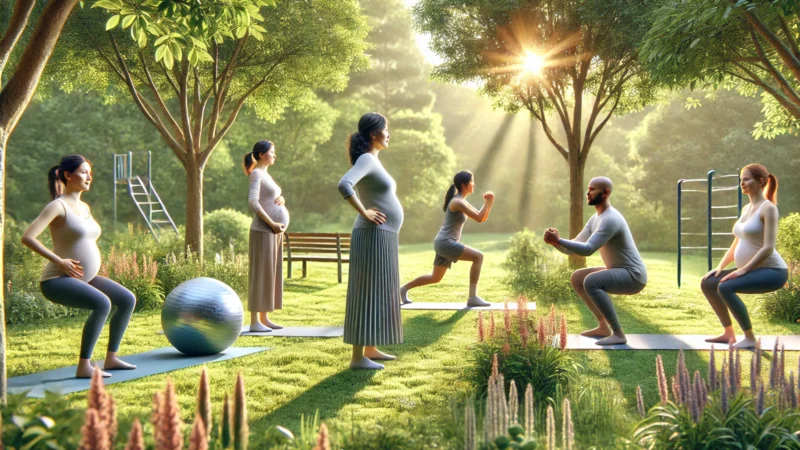
- Regular exercise: Activities like walking or prenatal yoga can improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control.
- Monitor blood sugar levels: Regularly check your glucose levels according to your doctor’s instructions to ensure they remain within a safe range.
- Use of insulin: If diet and exercise are insufficient to control your blood sugar, your doctor may prescribe insulin therapy.
Detecting and managing gestational diabetes early can help prevent complications for both the mother and the baby, ensuring a safe and healthy pregnancy.